Like what you see here? Our mission-aligned Girl Geek X partners are hiring!

Angie Chang, founder of Girl Geek X, welcomes sold-out crowd to LiveRamp Girl Geek Dinner in San Francisco, California. Erica Kawamoto Hsu / Girl Geek X
Transcript of LiveRamp Girl Geek Dinner – Lightning Talks:
Angie Chang: Thank you for coming out to the Girl Geek X Dinner at LiveRamp. My name is Angie Chang. I’m the founder of Girl Geek X. We’ve been hosting dinners like this for 10 years up and down San Francisco, San Jose. And I’m really excited to be here tonight to hear from these amazing women and to meet each other over dinner, drinks, and conversation.
Gretchen DeKnikker: So, we also have a podcast, if you guys want to check it out. Check it out, read it, give us feedback. Let us know, we have mentorship, intersectionality, finding career transitions, all of these things. So, definitely go and check it out. And this is Sukrutha.
Sukrutha Bhadouria: Hi, that was Gretchen. She didn’t introduce herself. Yeah, so we started off with dinners, we talked about podcast, and then we made it happen. In the meantime, we started to do virtual conferences, which we’ve had now one every year in the last two years. And fun fact, we now have what is…a Zazzle store with our amazing branded, cool swag, I don’t fit into the T-shirt that I ordered.
Sukrutha Bhadouria: But you could get tote bags, you could get cell phone covers, so it’s really cute. Or somewhere in the back, maybe, you’ll see what our pixie characters look like that up. But if you go to the invite for tonight, you’ll see these little characters that we have represented and we try to be as inclusive as well possible. So, all of our branding is very inclusive. Please share on social media, everything that you hear tonight from our amazing speakers. Use the hashtag Girl Geek X LiveRamp. And we will follow you and retweet and re share, so thank you so much for coming and thank you to LiveRamp.

GM of TV Allison Metcalf gives a talk on how LiveRamp got into the TV game at LiiveRamp Girl Geek Dinner. Erica Kawamoto Hsu / Girl Geek X
Allison Metcalfe: Hi guys, I get to go first. So my name is Allison Metcalfe. I am the GM of LiveRamp’s TV business. So just for context, what that means, LiveRamp, a couple years ago, we moved away from functional leadership 100%, where I was actually previously the VP of Customer Success. I’ve been here almost six years. I started customer success, I was patient zero A long time ago, and I will never do that again.
Allison Metcalfe: So a couple years ago–LiveRamp has historically been really, we really focus on the digital ecosystem and the cookie ecosystem. And there’s been a lot of changes in the industry that suddenly made TV a very, very compelling opportunity. And so, we launched a TV business that I run. And so, what I’m going to talk to you about now is kind of why we’re in this business and what the opportunity is and why it’s super cool. It’s really fun to be working in TV right now. And hopefully, we’ll get a couple converters from it.
Allison Metcalfe: So, TV is so crazy. Nothing has changed in the world of television in terms of how it was bought, measured, I need a timer here, sorry, in 70 years. So, literally like the way people measured TV and bought TV and demonstrated the success of TV up until a couple years ago was the same as it was 70 years ago, which is a little bit insane.
Allison Metcalfe: As you probably know, you think about yourselves, you are not watching Seinfeld at seven o’clock on NBC anymore. It’s not appointment viewing anymore, you’re streaming it, you’re watching TV really whenever and wherever you want, every single screen that you have, is a TV today, which is really great for us as consumers. Like TV has become very, very consumer friendly. But it’s caused a lot of problems for the industry.
Allison Metcalfe: So number one, is the way we’re measuring it, ratings is really hard to track now, right. Nielsen is the incumbent measure that would say this is how many people watched Seinfeld last night. They were able to do that because of a pretty archaic panel that they had and pretty archaic methodology. But it was accepted. And it worked for a long time. But now, the network–so it’s like NBC is, they’re putting all their money on This Is Us, right? And Nielsen is saying, “This is how many people watched This Is Us last night.” And NBC doesn’t believe them. Because they’re like, “What about all the people that watched it on video on demand? And what about the people that watched it on Hulu and Roku and all these other places where they could be streaming that versus just on appointment viewing, linear television?”
Allison Metcalfe: So, the audience fragmentation is making the networks feel like they are not getting enough credit for the viewership that they are actually driving that translate to they are losing money. And they don’t like that, right. The device fragmentation is also causing problems for brands, because the brands, all they want to do is reach you, right? If they are trying to reach young parents who are in the market for a minivan, they don’t really care where you are. They just want to make sure they’re reaching you.
Allison Metcalfe: TV used to be the easiest way to get phenomenal reach within one buy, right, because everybody was watching Seinfeld at seven o’clock and we knew who they were. Now, we’re all over the place, this creates a big problem. If you’re a brand. You’re like, “Oh my gosh, how much money do I spend on Hulu versus Roku? How much do I put on linear television? How much do I, what other devices,” there’s so many I can’t even think of them all. So, it’s a really big problem for the industry. But it’s good, right? Because change is good. And again, it’s very consumer friendly.
Allison Metcalfe: So what we call advanced TV, is the process of anytime we are using data and automation to buy and sell TV, which again, really was not done before, that sits under the umbrella of advanced TV. This is a roughly $80 billion industry–that’s the TAM in the United States. Historically, for LiveRamp, we made zero dollars from the television industry up until about two years ago.
Allison Metcalfe: So it was a whole new TAM for us, which is very, very exciting. Of that $80 billion that used to be bought and sold in the traditional way up until advanced TV came, now, we’re seeing projections of $3 billion being spent in addressable, which I will explain, close to 8 billion in OTT which is anytime you are watching television, due to your internet connection. It doesn’t matter if it’s on your phone, or your computer or your Smart TV. But if you’re watching it, because of the Internet, and not because of your set top box, right, that’s OTT.
Allison Metcalfe: And then, we’re also seeing a lot of companies like a really interesting trend is a lot of the direct to consumer. Companies like Stitch Fix or Peloton that are 100% digital companies are starting to spend a lot of dollars on television as more advanced strategies are becoming available to them. The other thing that’s happening here, guys, it’s really, really important. Facebook and Google are coming after TV hard, right. They’re like, “We want to keep growing at the rate we’re growing. But we already have like 80 or 90% of the entire digital ecosystem. So how do we keep growing, we’re going to steal money from TV, that’s what we need to do. And we’re going to do that by saying we have all the eyeballs that TV has anyways.”
Allison Metcalfe: And so, that’s another reason that the industry has to change to combat, Facebook and Google. And I think the demise of television is very overblown, as you can see by these numbers here. So, we power the future of advanced TV, when we talk about advanced TV, we’re talking about all of these things. So, addressable TV is literally the idea that you are getting a different ad, than your neighbor, right, Rachel here is big camper, I am not. You shouldn’t waste your dollars showing me commercials for camping equipment, but you should show it to Rachel. So addressable TV is meaning Rachel’s going to get the camping commercial, I’m not, based on my set top box, we power that.
Allison Metcalfe: Data driven linear TV is the idea of, if you have a target audience of say young families in the market for a minivan, we will match that against a viewership data asset so that the buyer can understand that young families in a market for minivans are over indexing to This Is Us and what’s another TV show? Modern Family, and they’re really not watching The Voice, or whatever it may be. So you’re still buying TV in the traditional way, you’re not targeting a household, you are still buying based on content, but you’re buying that content, because you are much more data informed.
Allison Metcalfe: I talked about OTT, digital video, this is clips, this is, Jimmy Kimmel had a great show last night, and there’s a clip of him and his funny joke and we might want to see, you’re all being forced to watch an ad. Before you can see that clip, as you probably all know. And then, probably the most important exciting thing is measurement. So historically, the way TV has been measured has been brand lift awareness, surveys, and reach.
Allison Metcalfe: Now, given the fact that LiveRamp and we have a couple other companies that can do this, too. We recently made an acquisition of a company called Data Plus Math, we can marry viewership data that’s ad exposure data to outcomes. So now Peloton, for example, can say, “Aha, my investment on This Is Us drove this many people to my website, that was a good investment for me. And I’m going to crank it up on This Is Us,” for example. LiveRamp plays in all of these places, a lot of companies that are getting into the TV game usually are only in one or two of these areas.
Allison Metcalfe: So it’s really exciting. I’m going to wrap it up there because we are a little bit crunched for time. And I’m not going to bore you with this. But I hope that was somewhat valuable and interesting to you. And thanks for coming. Thanks.

Product Leader of Global Data Partnerships Tina Arantes gives a talk on finding product/market fit at LiveRamp Girl Geek Dinner. Erica Kawamoto Hsu / Girl Geek X
Tina Arantes: Okay, Hey, everybody, my name is Tina Arantes, and I’m on the product team at LiveRamp. Been here about five years, so not as long as Allison, but enough to see us go from like 70 people in a little office in the mission to like, mission on mission to three floors here and like over 800 people. So it’s been a crazy ride and on products, we’ve learned a lot.
Tina Arantes: So I’m here to share with you some of the learnings from my product experience here. And primarily, the learning that listening to your customers is the first step in creating awesome products. So this may sound very obvious, like everyone’s probably like, “Duh, how else would you do it?” But when I’m out there like talking to other product managers through interviews, and other ways, it turns out a lot of people aren’t talking to their customers. And it’s actually super important because especially in the B2B business, like I’m selling into marketers, and I’m not a marketer.
Tina Arantes: So if I don’t know, if I’m not my own customer, the only way to figure out and empathize with them is to actually get out there and listen to them. So, I’m also a big fan of design thinking, right? So the only way you can create a product that your customer is going to want to buy is if you first empathize with them, define the problem you want to tackle, ideate to come up with solutions on how to solve it, and then prototype and test. So, the empathize part is actually like the part I’ll focus on first, which is like, how do you get out there and discover what are the problems your customers are actually facing?
Tina Arantes: So let’s jump right into it. How do you actually listen to your customers? The first step is actually just showing up. It sounds simple, but you’d be surprised how many times like you’ll have someone on Allison’s customer success team reached out and be like, “Hey, can you answer this question for this customer about this thing?” And the first thought most teams have is like, “I could, but how about that person does it because I have other important things to do with my engineers.” But actually, a lot of the times, it’s sometimes useful to take advantage of the opportunity to get out there and just meet the user, and start to establish trust with them. So you can ask them your own questions and get to know them better later on.
Tina Arantes: So step one is like just show up, make time in your calendar to find customers that are representative of your user base, and get to know them. So once you’re there, and you’re in the conversation, you can’t just jump right in with the hard hitting questions, right, you have to establish like base of trust. So warm them up, buy them a cup of coffee, introduce yourself, ask them about them a little bit. The way we do this, actually on a larger scale at LiveRamp is through customer advisory boards, where we actually organize getting some of our best customers together into a room, take them off site, somewhere that they can actually spend a few days with us, give us feedback on the roadmap and tell us about some of the biggest problems they’re facing.
Tina Arantes: And that’s been actually one of the really big sources of customer input and feedback that we’ve gotten. So you can do it on a small scale with a cup of coffee or organize like a whole event to get out there and start talking to your users. Okay, so once you have the customer, you warm them up. Don’t again, just jump in there with what you want to say, start listening to what they have to say, I don’t know how many times I’ve just been blown away by like being like, “Okay, what’s keeping you up at night? Like, what are your biggest goals? What can you not solve? Like, how can, how can we help you?” And they come up with all kinds of ideas I would never think of, sitting at my desk trying to imagine what they might want to do.
Tina Arantes: So be an active listener, listen to what they have to say. And don’t try to lead them to the solution you have in your mind. Because you know, you’re so smart, and you know how to solve their problem. But you also should ask juicy questions as well. So once you’ve given them a chance to talk, then you should have done your research and know who you’re talking to and know what kind of questions you can ask to really get at the heart of what you’re trying to solve.
Tina Arantes: So these could be like discovery questions, asking about what areas of problems they’re having to like, help you come up with solutions later on, that could be products. Or if you’re in a stage where maybe you’ve talked to a lot of customers, and you have an idea of a problem you can solve is like throwing it, putting it in front of them and seeing how they react to it. Do they get excited and be like, “Where do I sign? And can I buy this tomorrow?” Or they’re like, “Okay, that’s interesting, like, not that important to me right now.” So yes, you can ask your questions as well, after you’ve done your share of listening.
Tina Arantes: Okay, and after the interview, or after you talk to your customers, what happens next. Now the hard part happens where you have to map it back to everything you’ve heard from every other customer you’ve ever talked to. So definitely write these things down, keep them somewhere, like, I sometimes find notes from customers from five years ago, and I’m like, “Okay, that problem still exists, maybe we should solve it.” And then you start to look for trends, right? You want to see, is it a problem multiple customers are having, like, can I identify 20 customers that are having the same problem? How urgent is it for them?”
Tina Arantes: So people have all kinds of problems, but is it in the top three? Or is it like number 20? And they’re like, “You can solve it for me, but it’s not really going to matter.” And then the important part, like what are they willing to pay for it? You can ask like, “Hey, I have this next month, would you buy it?” And people will let you know, yes or no, there.
Tina Arantes: But let’s get real too, so earlier, I said like a lot of people don’t actually end up talking to their customers for various reasons. Of course, like time is always an issue as a product manager, because you’re running around crazy with your engineering team, like trying to keep sales happy, lots of internal squeaky wheels to keep from driving you crazy. But like you do need to make time to talk to customers. And even once you have the time, like I know, as a PM, all of these thoughts popped into my head, right? Like, what if they don’t want to talk to me? Who am I to like, go knock on the door of a Fortune 500 company and be like, “Can I have an hour of your time?”
Tina Arantes: But like, it turns out, most of the customers really do love talking to product and love providing their input in hopes that it will impact the roadmap and asking their questions to you as well. You can turn it into like a value exchange, like offer your thoughts on the vision of the product in exchange for their input as well. This one’s one of my favorite, like, what if they say bad things about my product? I know like, you get very attached to your work, right, and you don’t want to show up to a customer and they’re just like, “Yeah, no, I hate it. Your baby is really ugly.” Like, no one wants to hear that. Right? It’s terrible.
Tina Arantes: But it’s better to hear it so that you don’t walk around thinking your product is like, the best thing ever, when really like, there are some things you can improve. So, it will happen, like people will say bad things, you just have to deal with it and take the feedback as a gift. And then this one also comes up. I know a lot of product managers are like, “I don’t really want to get on the call. What if they asked me something, that I don’t know the answer to?” It’s like, that will also happen, like every single call, but it’s okay. You just have to be like, “I will find you the answer to that and pull in someone who does know the answer for the next call.”
Tina Arantes: So there’s a lot of resistance to getting out there and talking to your customers, but you got to do it. So what does it actually, what does success look like when you do this right? And when you don’t do this right? So maybe starting with like when you don’t do this right. Definitely over the past few years, I’ve made tons of mistakes, not vetting things carefully enough with customers. One standout in particular where we had a project and we’re like, “Oh, we’ll just make this product go much faster.” Because we had a few customers who were like, “Yeah, that would be great.” Jeff’s laughing back there, because he’s the engineer who built it.
Tina Arantes: So we built it, we launched it, and then no one wanted to buy it. And we were like, “What?” And it turns out, it was a problem for people, but it wasn’t something they were willing to pay for. So now, we always check like, “Oh, great, is the problem like how much would you pay for it at the end?” And it does work sometimes as well. So like we’re working on another product now that we actually got the idea from talking to our customers, different customer advisory boards, they’re like, “How can you help us share data between two partners? And we’re like, “Well, that’s an interesting idea, maybe we could help you there.”
Tina Arantes: And it’s turning out to be more successful and more people are willing to pay for it. Because of the hard work we put in, checking with a really large client base that this is going to be interesting or an urgent problem to solve and something they’re willing to pay for. So that is why I think listening to your customers, as a product manager is one of the most valuable things you can do. And the first step in creating products like people actually want to buy. So yeah. And we’re also hiring on our product team here. Definitely engineering team here. So if you want to chat later about any of this, I’m happy to talk more.

Software Enginere Eloise Dietz gives a talk on lessons learned from becoming CCPA compliant at LiveRamp Girl Geek Dinner. Erica Kawamoto Hsu / Girl Geek X
Eloise Dietz: Hi, everyone. My name is Eloise Dietz, and I’m a software engineer here at LiveRamp. I’ve worked here for about two years. And I’m currently on the data stewardship team. Our team is responsible for ensuring that LiveRamp systems use personal and company data ethically. And right now that means working to make sure our systems are privacy compliant. If your company works in personal data, you’ve probably heard of them, GDPR, CCPA. So I’m going to talk a little bit about what this privacy compliance looks like and why it’s relevant to software engineers.
Eloise Dietz: So first, a little bit of background. LiveRamp takes data privacy very seriously, partly because we think it can be a competitive advantage. We work in data onboarding, which means that we help companies advertise to their users online, which means that they can better personalize their ads online. Studies show that consumers actually really prefer this ad personalization and a more of a customized experience. And it can be a guarantee, or it has a higher likelihood of a higher return on investment. However, there’s also losing, people are losing trust in technology companies. And research shows a majority of people worry about how tech companies are using their personal data.
Eloise Dietz: In fact, one study found that 80% of people will leave a brand if they think that they are using their data without their knowledge. So companies in ad tech, like LiveRamp have to deal with this dichotomy. And they need a way to resolve this problem and gain trust back in their users. And I think that GDPR is a really important step in this direction. So, GDPR is a data privacy law that aims to regulate data in the EU, and it took place on May 25th of this year. So CCPA is kind of the California equivalent to this GDPR. And though it has many differences, it also incorporates a lot of the same ideas. It will take effect January 1st of next year.
Eloise Dietz: So a lot of other states are following California’s example, and also have privacy bills in the process. A lot of other countries are also inspired by GDPR around the world and are going through the process of introducing their own privacy laws. More are expected to follow. So as you can see, GDPR is kind of inspiring an overall shift in regulation of data privacy. And in the US alone, 68% of multinational companies have spent between 1 million and 10 million getting ready for GDPR. As CCPA approaches, only 14% of US companies say they are fully compliant despite its similarities to GDPR. They plan to spend another 100000 to $1 million becoming compliant.
Eloise Dietz: So we can see that these laws are really causing a big shift in how companies think about data. And the reason that is, or we can look into why that is by looking at some of the key GDPR requirements. Obviously, GDPR incorporates a lot more than this, but I thought that these were some of the most relevant to software engineers. So, the first is data minimization. Or the idea that we should only collect the data on users that we need to solve a certain task and then delete that data as soon as the task is accomplished.
Eloise Dietz: The next is that data subjects or individuals have certain rights to interact with their data. So they have the right to access the data or retrieve all the data a company has on them, they have the right to restrict processing of that data or opt out, they have the right to delete that data. And they even have the right to rectify the data if they think it is incorrect. Then finally, users have the right to be notified of data collection and the use, that data is going to serve. And if you got a ton of updated privacy policies this year, it was probably from this part of GDPR.
Eloise Dietz: So you seem kind of like standard practices. But they fundamentally change how a lot of companies think about data, the companies in a data graph mode, they might not even realize what personal data they have on people, nonetheless, what it’s useless for and how to collect it and return it to an individual if they asked for it. So this is what data privacy does not look like and what data privacy actually looks like is constantly asking yourself these questions as you build systems.
Eloise Dietz: So the first step is understanding what personal information that you have, and that your system processes. Or associating with that data, why it was collected, where it was collected, and what use it’s going to serve. Data minimization is probably one of the most relevant to software engineers. It means reviewing your data and deleting it, when it is no longer needed. But this also means not logging, personally identifiable information, it means when you store it, not storing it raw, storing it pseudo anonymized, means restricting access to that data to only those who are required to use it.
Eloise Dietz: And it means not using real data in your dev and staging environments. And finally, also automating user rights for deletion, restriction, processing and access. And so at LiveRamp, as we kind of went through this checklist of how to make our systems privacy compliant, we realized that there are some cases where we even need to go beyond the law, beyond GDPR and CCPA, in order to design for the privacy of the end user, not just designed to make our systems compliant by these privacy laws.
Eloise Dietz: So the first one of those instances was reading a privacy vision to hedge against the many data privacy laws that are expected to come out. So, for example, these laws are going to differ. CCPA and GDPR differ in many ways, and sometimes, even completely contradict each other. One example of when they differ, is this right to opt out. So CCPA says people have a right to opt out of data processing, whereas GDPR says people need to actually give their consent and opt in before data is allowed to be collected.
Eloise Dietz: I think that for users, understanding the way that you can opt out. So many different privacy laws is an undue burden on the users. So, LiveRamp decided to have a global opt out repository, where we, if someone wants to opt out an identifier, say a mobile ID, cookie, or email, we pseudo anonymize that information and store it in a global repository. This means that deployments in the EU as well as nationally in the US can check to ensure that they’re not processing data over any identifier that is in this global repository. So going beyond the laws and having a clear privacy vision that opt outs will apply globally not only made our LiveRamp systems more straightforward, but also ensures that the end user is actually receiving the privacy that they’re expecting.
Eloise Dietz: Second, never let privacy come at the expense of security. So in the effort to make users be able to better understand what data companies have on them, laws like CCPA and GDPR may actually be opening up this data to bad actors and more vulnerabilities. For example, the right to access their own data means that someone could make a fake this request and maybe receive another person’s data. So I think users may not understand that this security is at the risk of privacy. And it’s up to the, this privacy comes with the risk of security and it’s up to companies to make sure that this does not happen.
Eloise Dietz: So finally, embedding privacy into the user experience I think is an important place companies can improve on. So especially the ad tech ecosystem is incredibly complicated. This infographic shows the number of ad tech players has increased significantly over the years. Users shouldn’t have to understand how all 7000 players interact in order to understand their data privacy rights. A survey went out after GDPR that asked users what their biggest complaints were and the study found that most people’s biggest complaint was the long overcomplicated privacy regulations.
Eloise Dietz: And though these may be required, sorry, privacy policies. And then though these policies may be required by law, I think that the system should be designed to incorporate the end users privacy in mind, and make it easier to work with the systems in order to find the best privacy policy. So this doesn’t necessarily mean having a accept all or opt out of all policy that often doesn’t work with like most people’s privacy. And it also doesn’t mean having so many different privacy settings where you really have to understand the privacy law in order to understand what you want. It means designing for the end user and creating a concise, intelligible, transparent and easily accessible way of working with the privacy, working with your own privacy settings for that company.
Eloise Dietz: So my end takeaway is to take GDPR and CCPA as a way to rethink your data usage, but also looking beyond these privacy laws and consider the end user when designing your systems in order to truly protect their data privacy.

After bites and drinks, girl geeks enjoyed lightning talks from women in various parts of the org at LiveRamp Girl Geek Dinner. Erica Kawamoto Hsu / Girl Geek X
Akshaya Aradhya: Now, that the first half of our session is over, does anybody have any questions for the speakers?
Audience Member: Quick question for you. I actually didn’t realize data minimization [inaudible] example because [inaudible] users [inaudible] out [inaudible] that even an option [inaudible] data minimization?
Eloise Dietz: A user opts out, as in the fact that we’re still maybe storing like a pseudo anonymized identifier?
Audience Member: Mm-hmm (affirmative).
Eloise Dietz: So the idea is that personally identifiable information, I think this is right. The idea is personally identifiable information needs to be minimized. But when you pseudo anonymize an identifier, it no longer counts as personally identifiable. So by storing that anonymized version, it no longer kind of counts as the process, I believe, is for opt outs.
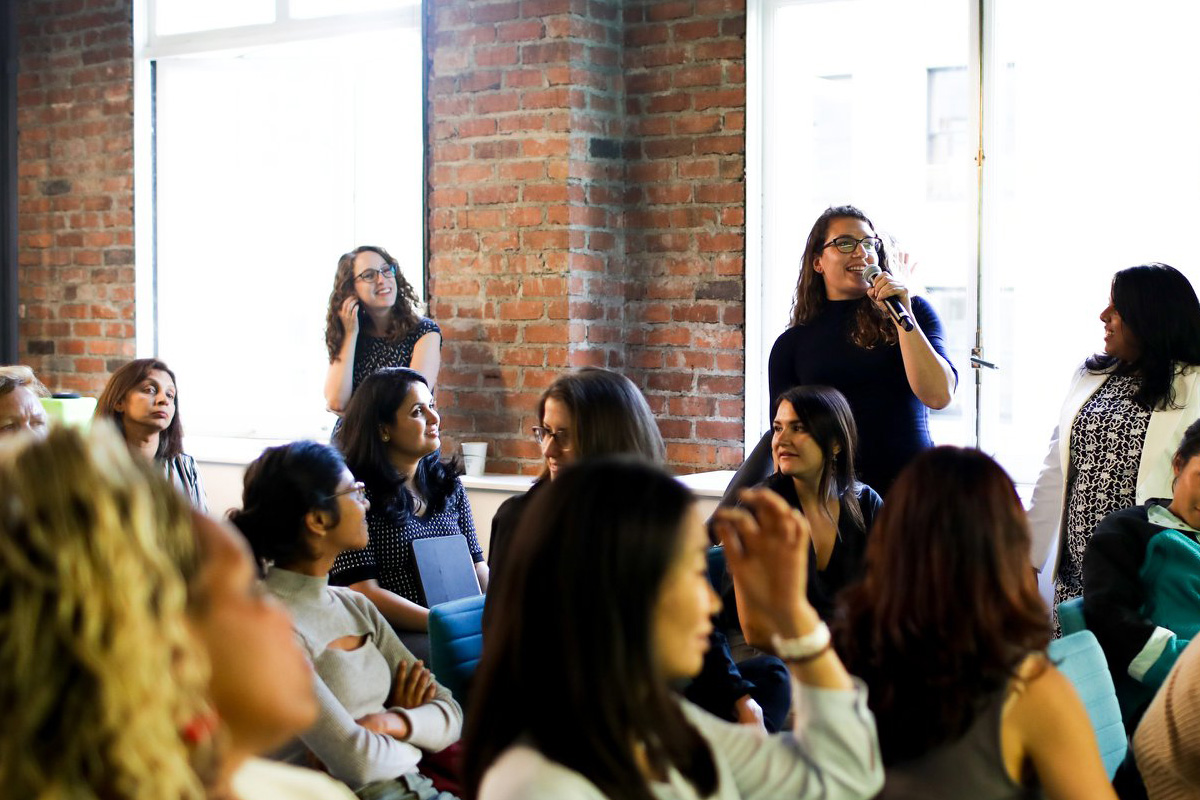

Software Engineer Erin Friesen gives a talk on destroying an entire build ecosystem to leading the engineering wide initiative to protect and improve that very same system. Erica Kawamoto Hsu / Girl Geek X
Erin Friesen: Hello, I’m Erin. I’m a software engineer on the infrastructure Platoon, I’m working [inaudible] DevOps. And I have an obsession with making builds easy. It’s absurd. All the engineers here can say that I’ve authored them with everything. So I’m going to talk about how I got to that point, and a lot of the mistakes I made along the way. So next time, you have to do a migration, you don’t have to do them.
Erin Friesen: First off, I’m going to be talking about Jenkins. Jenkins is my best friend. If you don’t–anyone here know what Jenkins is. Yeah. So Jenkins is basically a tool to get servers to do what you want them to do. If you’re like, “I want to deploy this, send it here. I want you to set a cron job, do this, I want you to build this do this.” That’s what it should be. So we start our journey with a horrible Slack message. I snapshoted the wrong thing. And I don’t have a backup, and we don’t have our configurations. We’ve lost our builds.
Erin Friesen: As you can see, Jenkins is on fire there. And our last backup had been 10 months previously, record everything on the master server. And we had just demolished that. So we panicked, we figured it out, we got our builds back, but realizing that we are storing our configurations, the core thing that we need to do to deploy on the thing that if it goes down, it breaks it, not the best situation. So, we came up with a solution, Jenkins files. So basically, it’s codified builds, you put a Jenkins file into your git repository, it lives there, you can take Jenkins down in a heartbeat. I almost did that as a demo. But I didn’t want all those users to panic.
Erin Friesen: And instead of storing your configs in a UI like this, you get seven to eight lines of code. And that’s your entire build configuration, which is pretty awesome. And it’s very replicable. You can version your code, you can pick a library, it’s so much more control over your environment. So previously, these are my steps to get there. Let me say this was one of my first larger, like known visible projects that I’ve ever lead. Here are my steps. I create a product, I just have the teams do it themselves. And then I’m done. Easy, right? Not quite.
Erin Friesen: So first off, I skipped over scoping out the size of the migration. I didn’t realize how large the project was and how different it was. I’ll give you a scope. We have over 250 Java repositories, you have over 150 Ruby on Rails builds. All of these builds have PRs and master builds. So if you do the math, that roughly puts the 700 things that you have to migrate, that you can’t break because if production breaks, you can’t deploy a fix, you’re in trouble. So I didn’t scope out the size of the project. It led to some very troubling times.
Erin Friesen: And the second was, I did not ask for input from engineering team until I was well into development, a lot of about listening to your stakeholders. I didn’t know what they needed, or what they actually wanted from their builds. But I was like, I know better. I’ve seen a Java build. You’ve seen one Java build, you seen them all, right? No, that’s definitely not the case. And lastly, I didn’t ask anyone for help about their experiences with it, what they’d done to actually build it, other people had experienced Jenkins, but I sort of ventured on my own thinking I could plow my own path.
Erin Friesen: That didn’t work out too well, either. And so, a lot of this boils down to I didn’t communicate with people. I didn’t ask them, and I broke a lot of things. And I’m still very sorry, you guys are watching this later. And I think lastly, I assumed that the teams would do the work. Like, I assumed that if I presented the seven lines that I needed to do, everyone would adopt it, everything would work, and everyone would go in the same direction at the same time, and it would be fine. That’s not it. Because guess what, everyone’s builds are different. They’re unique. And they’re just different and unique.
Erin Friesen: And I assumed they would do that. I also didn’t assume that they didn’t want what they had, they wanted something better. Like, you want to build your own solution. And you want to have power over how you deploy and where you deploy. And I didn’t listen to any of that. I mean, I didn’t listen. I also pushed changes without telling people because I didn’t version at first, it was, I didn’t listen, and I didn’t communicate with the team. So that was like the biggest thing if you to take away anything from migration over communicate and like, talk to everyone, and I mean everyone.
Erin Friesen: So these are my steps to a new successful migration. Do your research. I didn’t. So, I didn’t break down my problem. I didn’t even figure out where my share was like, what? Where should I be living? Like, what needs to get done, and what’s broken? What can stay broken? And talking to everyone, I just didn’t think about it. Didn’t break down the problem into injectable sizes. And I couldn’t get the iterative feedback because I didn’t check. I was like, “I’m going to roll into this. And it’ll work.” Which leads into break up the project into bite size. Because if you know what you’re getting into, believe it or not, you can break it up into smaller parts.
Erin Friesen: I’m a rock climber. And so, whenever I go outdoors, I go, and I look at the mountain. I’m like, “Cool, what do I need? I need to be able to solve this section of the climb and the section of the climb.” And this is how I get to every single portion. And I always break it down into bite sized steps because you’re like, “Oh, it’s only one reach, or two reaches or I don’t know, a high knee, like pick a move.” And it works a lot better to get to the top.
Erin Friesen: And if I haven’t said it enough, communicate, just communicate with everyone. I didn’t get feedback early enough. I didn’t iterate on feedback. And I created a doc, a roadmap for it. When I’d already been working on the project for four months, like that wasn’t the efficient way to do it. I got excellent feedback from stakeholders. But it took me too long to get to that point of starting a feedback cycle.
Erin Friesen: The next two come hand in hand. Rollout gradually. And at one point in time, I had 355 PRs open, various repositories, so I created a script to create a PR to inject my one size fits all Jenkins file. And there was no back out, like it’s hard to rewrite those. And it was broken, it was hard because I didn’t version it, I didn’t have an interface. And so, if I had to make a change to a function, I had to make 355 individual commits to everything, they’re starting to get customized. So I didn’t have a rollout plan, which means I also didn’t have a backup plan. If I needed to roll back what I was doing.
Erin Friesen: So, successfully, you need to have backup, you need to be able to bail if a rollout goes bad. And finally, you just iterate and repeat over and over and over and over again. And if you keep these steps in mind, the best thing is, everyone wins. Everyone gets the product they want. You don’t waste cycles on trying to build something that they don’t want. And you actually get help along the way and it speeds it up. So that was me about how to migrate way better than me.
Akshaya Aradhya: Questions for Erin?
Erin Friesen: Part of it, the story, oh, it didn’t have the date on it. It was 2018. November, 2000–no, November, 2017, it was right at the end.
Akshaya Aradhya: Before Thanksgiving, okay. Any other questions? All right.
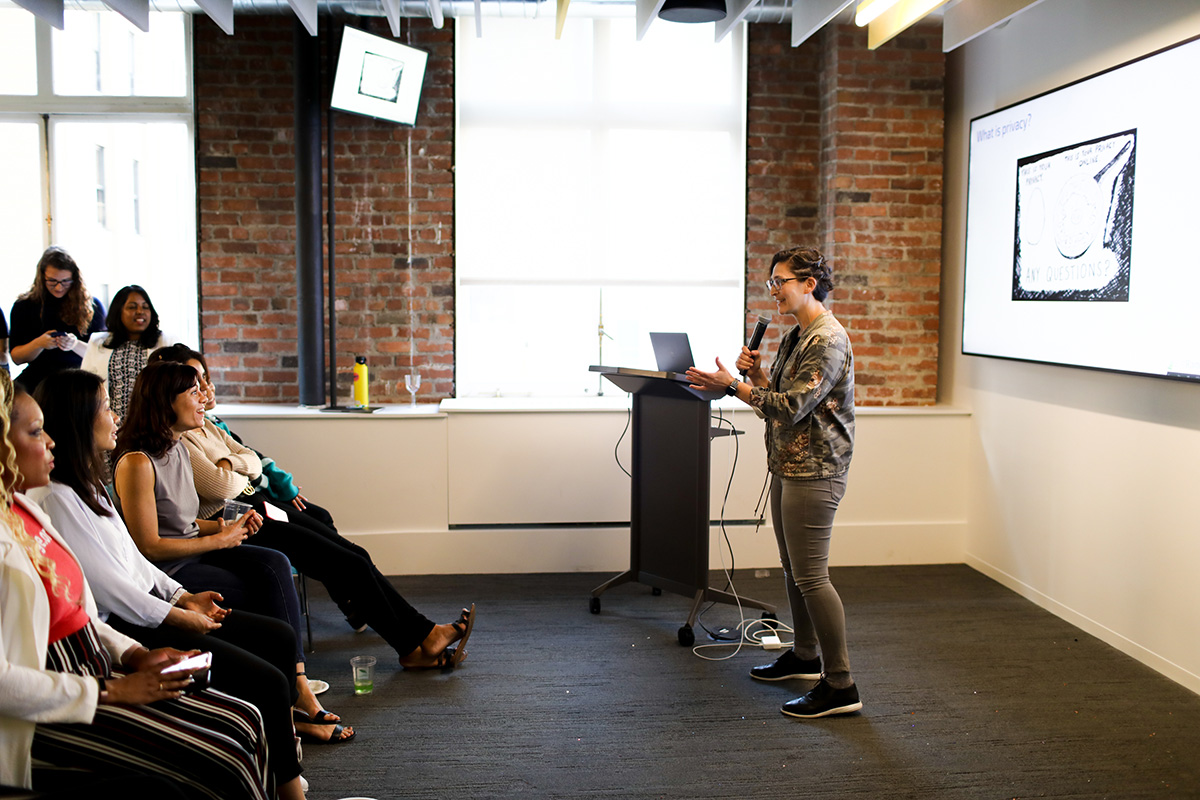

VP of Product Rachel Wolan gives a talk on the evolution of privacy, discuss what it means to build products intended to protect consumer privacy globally, and the design decisions we make along the way. Erica Kawamoto Hsu / Girl Geek X
Rachel Wolan: Hey, everyone, my name is Rachel Wolan. And I’m the VP of Applications for product. And I’ll echo what Tina says, we’re hiring. I’ve been here about five months. And I think Eloise did a great job of kind of helping everyone understand a lot about the regulations of privacy. Today, I’m going to talk a little bit about, like the history of privacy. So I will kick this off by telling you a very private story.
Rachel Wolan: So maybe over Christmas, I got engaged. And before I asked my partner to marry me, said yes, I had to get through her parents. And I was way, way more nervous about this stuff than talking to her. I’ll tell you a little bit about her parents. They’re from Singapore, they’re native Chinese. And I’d met them twice. I had a lot of things going for me. So, I sit down with her parents. And I’ve managed to, it’s Christmas. And I got all the kids out of the house, like they went to the bathroom, is great. I had like 15 minute window.
Rachel Wolan: And I was really looking for, not permission, but their blessing. So I sit down with them. And I say, “Hey, I’d really like to ask your daughter to marry me.” And mom’s like, “Hey, I’m going to sharpen my pencil.” She like, basically pulls out a list of like, 20 questions that she wants to ask me. Just asking me what were your past relationships like, what, like, do you have kids? I’m like, “No, no kids,” “Do you want kids? When are you going to have kids?” Like, all these questions.
Rachel Wolan: And like I think I’m doing a really good job. And this whole time, she’s actually translating in Cantonese to Mr. Chia. And I think, okay, I’m like, her mom’s like holding my hand, things are going really well. And I’m like, “Okay, this is over. She’s about to give me a blessing.” And then all of a sudden, Mr. Chia’s English gets really good. He looks at me, and he says, “What do you do for a living? How much money do you make?” And this is not something that like even I talk to my parents about. And it kind of struck me that privacy is really contextual.
Rachel Wolan: And I tell this story because privacy isn’t like one thing. It’s not something that is just regulated by one country or a group of countries, it’s something that is very meaningful to each individual. It’s different based on your race, your age, your gender, your socioeconomic status, your sexual orientation, where you live, where you’re from, like what religion you grew up in, really everything. And privacy is, each person’s privacy might even change over time.
Rachel Wolan: And, what I think is also, like, an important context about privacy is it’s a relatively new concept. So I’m going to show you guys some really cool technology that has helped evolve privacy. So the first is the printing press. The silent reading was really, one of the first forms of privacy, where people kind of had like, internal thoughts that they weren’t there, maybe they were writing them down, maybe they weren’t writing them down. And that really took like, 500 years to evolve.
Rachel Wolan: Internal walls were huge for privacy. Previously, it had been like, kind of that one room house where people lived, and they kind of all slept in the same bed for a long time in the entire house, and, like, fast forward to the 1900s. And the camera came around. And the concept of the right to privacy actually came to being. And what I think is interesting about this is that we didn’t really even put laws into place around privacy until post Watergate, right, like 1974.
Rachel Wolan: And then fast forward to today, AT&T, is, like, you can pay AT&T 30 bucks to opt out of ad tracking, but most people don’t do that. It’s really, the concept of privacy has evolved. And, I think, really, you have to think about privacy from like the standpoint that there’s a value associated with privacy and people are willing to trade privacy, there is a currency. And how many Millennials are in the room. If I offered you a pizza for three of your friends’ email addresses, would you… That’s what I thought.
Rachel Wolan: And so, I just spent a couple of weeks in China. And if you go to almost any street corner in China, you will see these cameras. And what they’re basically doing is tracking, what do citizens do? Did they walk across the street, did they jaywalk? I jaywalked, like this morning. So my social score will go down. Did they go through a red light, and all of these characteristics are being collected as part of a social privacy score, right, a social credit score. And so, really, in this case, one of the reasons why China introduced a social credit score is because in 2011, I think I saw some stat, two out of three people were unbanked in China, they really wanted to accelerate, people getting credit and being able to buy houses.
Rachel Wolan: And so in 2015, they actually made their data, their privacy data available to eight companies, including like Ant Financial, which is owned by Alibaba. And so today, I was talking to one of my co workers about his social credit score, and he was saying, “Well, I definitely don’t yell at my neighbors, I don’t park in a parking spot that’s not mine. Because that’s going to ding me and I want to, use the whatever the version of TSA Pre check is, right, if you have a high social credit score, you get a better line at the airport, there’s a different car on the train, there’s even a different–you can like skip the line at the hospital.” So there’s a lot of benefits. And, really like privacy can be traded for societal value.
Rachel Wolan: So, then the question is, I did a lot about design in our product org. How many people here have designed apps for Android or products for Android? So you know it’s really freaking hard. And I would say designing privacy is a 10X problem of them. And so, this is actually was a pizza study, where people were, there are 3000 people that were asked to trade their friends’ email addresses for pizza. Like 95% of them did. And that’s kind of like what I think is interesting here, because Tina aptly said, like, ask your customers what they want.
Rachel Wolan: But the most interesting thing about the study is customers actually said, “Oh, no, I would never do that.” Like the people in the study said, “I would never get my private information.” And then they target those same people. And they all did. So, this is one of those situations where you really have to actually think–was anybody in here familiar with privacy by design? Cool. So privacy by design is, it is a framework that you can use in order to start thinking about, does my product really protect the privacy of… So you can think about it at the very beginning and discovery and start asking questions, to try to understand the needs of your users. And look at it as kind of like a review process. We have a data ethics team at LiveRamp. We have what’s called a cake process where you can actually start to think about like, a probe through right before you even start building. Does this match our privacy standards?
Rachel Wolan: And then, I think a lot of the government laws that have been put into place, right, from the perspective that it raised our awareness of–around privacy, but it’s really our responsibility. And so, I’ll leave you with one final thought. So, this is actually privacy. Our phones are just like spraying our private information at all times. And so, like, try this, like brief experiment, turn off location services on Google. Does it still work? So I did this for like two weeks, and it kind of drove me crazy. And what’s interesting about this is, I actually had to go into a separate set of settings to completely turn off location services.
Rachel Wolan: And the cynics may say, “Oh, it’s because Google wants to track you. They want like all your data so they can sell your data, blah, blah.” And I actually think that this was really a design decision. Because they knew that you actually want that blue dot. And you want that blue dot, because you get value from it. You’re willing to trade your value, and maybe even go and kind of look and see. Like maybe you don’t want to trade all of your location data, but maybe some of it, for that value exchange. So, in conclusion, treat data like it’s your own, and make privacy happen by design. Thank you.
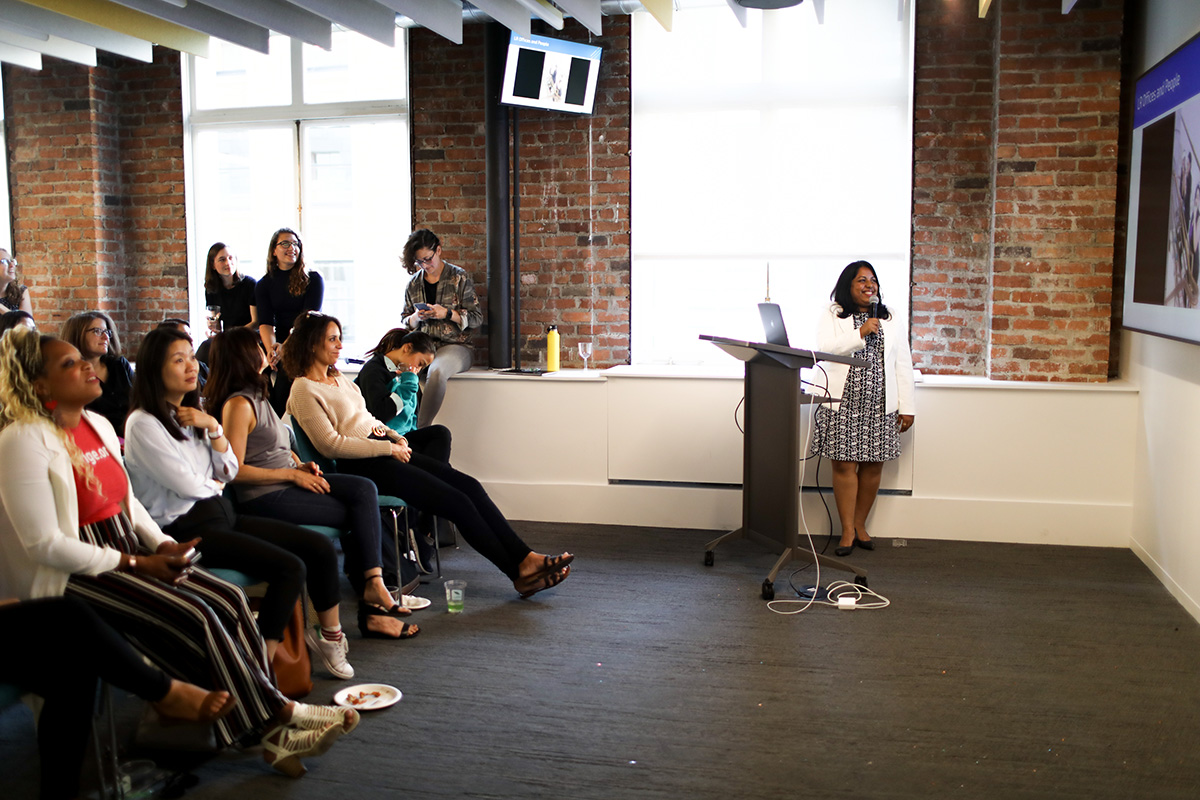

Senior Engineering Manager Akshaya Aradhya gives a talk on managing a geographically distributed engineering team at LiveRamp Girl Geek Dinner. Erica Kawamoto Hsu / Girl Geek X
Akshaya Aradhya: Hello, everyone. My name is Akshaya. I’m the IT manager for the integrations group. And I work with people like Jeff, Sean or head of engineering, Andrew, who’s our biggest women ally, here. He has three daughters. And when I told him we are hosting a Girl Geek X event, he’s like, “Woo-hoo.” So, that’s Andrew right there. And Jacob, who’s in my team, he’s awesome. And he’s supporting all of us. And I work with all these people every day. And I want to talk about how I manage distributed teams. And my of champagne.
Akshaya Aradhya: That I want to give a glimpse of how many offices we have globally. So these are camping experience. We have social, there’s a doctor in the office. We have a lot of fun [inaudible]. Our New York office, we’re on Fifth Avenue where all the shopping malls are. Philadelphia. Seattle. Burlington. Arkansas. Erin Bodkins was supposed to be here. But she had another commitment. Paris. There is a lot of French people in my team. London. Asia, Pacific, China [inaudible].
Akshaya Aradhya: Because I knew how loud they were. So, let’s talk about all these teams that you just saw, right? So I manage two teams, I’ll soon be managing four teams. And most of the, like both the teams that I manage are currently in within United States right now, but may spread out to China. So this is the headquarters where most of my team sits, but not all of them. There are some people out there in the New York office. And there’s one in Philadelphia, and, I also talk to the people in Arkansas, because I like them, you saw how fun they were.
Akshaya Aradhya: Some of my team members, like I said, are French and they like going back to France to meet their family and sometimes work out of their homes. And is that normal for LiveRamp? Yes. But you don’t necessarily need to be French to work out of your home. So what do I do first thing as a manager, whenever I, start managing any team, I do it inside, listen first, so I kind of ask them, what are their preferences? Do they have any time commitments? Some people have kids, they need to leave at certain times, some people have soccer practice, some people need to work out for health reasons or for any other reasons.
Akshaya Aradhya: And some people, like not having meetings at a certain time, and we chat a lot during our one on ones. Jacob is nodding his head. He knows why. And so, we have all these preferences. And East Coast people have their preferences. So, how do I manage the priorities? Like how do we all deliver against this shared vision? So, I can go back and make notes. And I’m like, so if we have dedicated set of meetings for the team to talk to each other, that’s number one. You’re all one team. You all need to get along, whether you like it or not. And you need to talk. And how do you establish that, right?
Akshaya Aradhya: Before I started working for LiveRamp, I was working for a company called McKinsey right across the street. And before that, Intuit, and it’s like, each company has its own culture.
Akshaya Aradhya: At that time, I was married, but I didn’t have kids. So just a piece of cake, right. And then I got pregnant, and then they flew me to Canada, ask me that went. My feet swelled so badly, I couldn’t fit in my shoe. And not that… And I sent a picture to my husband, once I, or two different shoes. And I couldn’t even see it. You know? And I was like, “Yeah, yeah, sure, right. The time difference, just wake up when you’re pregnant, you love waking up when you’re, like then and you like everyone you meet when you wake up. Right?”
Akshaya Aradhya: So that’s how that went.
Akshaya Aradhya: The culture doesn’t mandate you to go and sit with someone to be productive. You could as well be on blue jeans. You can, like I made my son’s appointment after joining LiveRamp. And then I could come back can take meetings, take knowledge transfers, talk to people, be productive.
Akshaya Aradhya: You’re not judged based on where you work from. Okay, that’s number one. Second thing, as a woman who went through all of this, I kind of make sure that I don’t step on other people’s toes or schedule meetings when somebody has an important thing, okay. And if you’re working with East Coast people, I tell all my teams, you better have those meetings, before 2:00 p.m., Pacific, otherwise don’t have shared meetings. And if you do want to have shared meetings, ask that person, if it’s okay, get the Slack message saying yes, and then you’re going to have that meeting. And, make sure that you don’t keep it as a recurring one. So that’s one thing, coordination.
Akshaya Aradhya: And following the right tools, I mean, you need to, whether you follow Agile or [inaudible], whatever it is, or whatever form of Agile your company follows. I know, Agile means different things for different people. But you need to get your message across to the team, everybody needs to talk, at least for like 10 minutes a day, and share what they’re doing. And, like, after sharing work related things, you want to share anything personal, or any, anything that you want our team to know, like you are engaged or you have a baby or whatever it is right, you can now share it.
Akshaya Aradhya: And, in one of my teams, I tell people, right, just because you’re working out of San Francisco doesn’t mean that you need to sit here till I leave, or sit here till 6:00 to make a point. You’re going to work on flexible time. And I need to see what progress you made. And you’re not blocking anyone and you’re out, right. It’s value to your personal space and time while being productive and accountable. That’s what you need.
Akshaya Aradhya: Again, I’m going to share my version of what works and what doesn’t. So you can as will be micromanaging, go to each person’s desk. Or like you could start off by not asking questions, or over communicating, assuming things and get the wrong thing. And then pass it on to your team, you lose that trust, you lose that trust with, it’s so easy to lose trust when you’re managing distributed teams, then micromanaging. Who loves these people in this room? That’s what I thought. And then people start leaving, and you wonder why and the cycle repeats, if you’re not listening, if you’re not watching your team, the cycle repeats. What works?
Akshaya Aradhya: Get the wrong thing. But you learn and adapt. People make mistakes. It’s okay, as long as you’re not consistently making them, you’re okay, you’re going to learn. And you’re going to share what you learn. Sharing is not on the screen because I run out of space, but you got to share what you learn with your teams, and communicate closer. Talk to them drop. Messages on Slack or whatever messaging service you use, add any relevant process. Relevant process, not process for the sake of process. And relevant process that works for you and whoever you’re working with. Are you peer programming? Are you a software engineer? Does this process work for you? Fine. If you’re in product, maybe you’re talking to customers, there’s a different process that Tina or Rachel may use, I don’t know.
Akshaya Aradhya: But as engineers, especially here in the valley, or New York or all the places that you work, whatever works for you is the best process. That’s what I tell teams and effective collaboration, effective collaboration. Destructive feedback is not effective collaboration. Rambling is not effective collaboration. Putting down others, sarcasm, you’re maybe the best, most intelligent person. But if you’re not nice, you’re out, that’s good as that. So play nice. And teamwork. Teamwork is success according to me. If you don’t work as a team, you work in silo, you may be the best person in the world. But if your team doesn’t see what you do, or if your team doesn’t find value in what you do, you don’t have any business value with the work you’re doing or you don’t grow, you don’t let others grow, you don’t help anybody or mentor people. That’s all contributing to bad culture.
Akshaya Aradhya: One of the things that I really like at LiveRamp when somebody spoke, during my onboarding, was that if somebody sends you an email, you respond quite quickly. It’s–in other companies that I worked at, response right away meant that you’re supposed to work or respond back at some time, right? So now studying at Wharton, Sean, our head of engineering. At his level, or Andrew or even Jacob or who, or Jeff, if you send a message to them, and I work from 1:00 a.m. to 4:00 a.m. because I need to study when my son is sleeping. Some of you may resonate with that. So if you don’t, you can judge and I’m crazy, partly.
Akshaya Aradhya: But that’s my time when both my dogs are asleep, and my son is asleep. That’s my time. Okay, so what do I do? I catch up on all the emails and I told my team, “If I send you a message on Slack, or an email, do not respond to me outside office hours, unless it’s really urgent.” There have been nothing really urgent that needs a response. And I was surprised when I sent a message to Sean one day, and he just responded at 2:00 a.m., I’m like, “What did I see? Did I a response?” And I’m like, “Thank you for messaging.”
Akshaya Aradhya: And it’s like, you may choose to do that. But it’s such your own volition, you’re not forced. And I think I tell all my teams that, “If you see it, ignore it. If you don’t want to, like if you’re sleeping do not wake up, because of me. Snooze your notifications.” Yeah. And basically, there’s a saying, right, you don’t go to work when, something you really like, then you enjoy what you’re doing. It’s not really work or something like that.
Akshaya Aradhya: And I think when you join a company that values your personal space, your ambitions and offers you opportunity to grow. And you love what you’re doing. There was recently a job satisfaction survey at Wharton, where I’m studying, part-time. It’s like, in my group, and when I say group, it’s about seventy people in one section. People did a job satisfaction survey based on so many different metrics. And they were talking about organizational stuff, and how do you grow your teams? What is effective, what’s not, somewhere on this, but in a more lectury fashion.
Akshaya Aradhya: And I took a survey of my past job and this job. And it was one among the top five. And I’m thinking, “Huh, I did that, I think, right?” When you love what you do, your stress goes down, you’re happier, your kid kind of sees you really happy, right? You don’t go crazy. And you can actually do what you want to do, study, pick up a hobby, rock climbing, or do a side project on Android, I don’t know, on whatever you want to do. Don’t do that. So yeah, it’s like, the last thing I want to leave this room with, is like this.
Akshaya Aradhya: Professionally, you set an example for your team. You don’t need to be a manager, each person can be an individual. You set an example for your team. And if you overburden yourself or you don’t enjoy what you’re doing, your team can see it and your productivity goes down. So make sure wherever you choose to work or whoever you choose to work with. Hopefully at LiveRamp, because we have opening, you should choose something that will allow you to grow and be happy at the same time. And that’s what the whole talk was about and what all the speakers and organizers want. And hopefully, after this presentation, you come by and say hi to all of us and hang out with us, ask us questions, learn about us and connect with us. We would love to keep in touch, any case. Thank you.
Our mission-aligned Girl Geek X partners are hiring!