Like what you see here? Our mission-aligned Girl Geek X partners are hiring!
- Check out open jobs at our trusted partner companies.
- Watch all ELEVATE 2023 conference video replays!
- Does your company want to sponsor a Girl Geek Dinner? Talk to us!
Angie Chang: My name is Angie Chang and I’m the founder, co-founder of Girl Geek X. I’ve been organizing events in the San Francisco Bay Area for over 15 years, and this is our first virtual career fair. I wanna take a little bit of time, one minute away, from our keynote speaker to talk a little about the sponsors that are supporting us today, cuz they are hiring and as you know in the headlines, there are layoffs and your friends are probably looking for jobs. Please tell them about this free event that’s happening right now today!
Angie Chang: There are recruiters from Autodesk, Cadence, United States Digital Service in Washington D.C., CodeSee and Dematic. And I’m gonna tell you a little bit about their booths. If you wanna go check them out at 12:00 to 1:00 PM today, there’ll be recruiters there. A quick rundown of those booths, I walked around this morning and they look amazing. You should go look at them and meet the people at these companies. They’re very friendly and they love answering your questions about the industry, their jobs, what it’s like to work there, how to get your resume into tiptop shape.
Angie Chang: I hope you’re going to a lot of the sessions today are very, very useful toward getting your resume and interview to be in a place where you can be successful. So Autodesk’s Booth has round tables with recruiters from Tech, Sales, and G & A. They also have a women’s group network that is gonna be there. So please go talk to them at noon to 1 Pacific time. There’s also Cadence and they have round tables for Cadence Careers and to learn about Cadence, culture or life at Cadence. So please go check out Cadence Booth at 12 PM to 1 PM today.
Angie Chang: United States Digital Service in DC has posted round table times in Eastern Times, so I’m going to just tell you them Pacific Time cuz that’s where I am and I had to do this math this morning. The design table is currently, I think occupied and there’s someone there in the USDS booth. They have a Talent roundtable at 10:00 AM Pacific. They have a Product roundtable at 11:30 AM Pacific. And their Engineering roundtable, if I’m doing the math correctly, is 12:30 PM Pacific Time. Go check out the USDS booth for their tables at those times. And CodeSee’S Booth has posted a sign that they’re in the lounge and that their CEO is going to be giving a developer workshop at 11:30 AM Pacific time today if you wanna learn about how to stand out in this job market, for developers who are current and aspiring.
Angie Chang: And last but not least, Dematic’s booth has a round tables about Culture and Dematic Careers. Please go check out their booth and talk to their recruiters and staff today in their booth. I saw the lounge table, they had lots of people there, so go talk to them when you have a chance. They’re really great and nice people.
Angie Chang: And now it’s time to our keynote speaker. So without further do, I am going to introduce you to Judith Syau. She is a senior software engineer at Stripe. She works on internal tooling and prior to Stripe she worked at startups in IoT and Consumer Marketplace and she’ll be talking to us about understanding company’s culture before accepting a job offer. So welcome our keynote speaker, Judith!
Judith Syau: Thank you so much Angie. Thank you all for joining and hope you’re having a great time at the Girl Geek X Elevate Conference so far. My name is Judith and I’ll be talking about how to understand company culture before accepting the job offer, so hopefully you can come out of this session with some useful tips and tricks that you can use throughout the rest of this conference and beyond.
Judith Syau: My name is Judith, I use she her pronouns, and I’m a software engineer at Stripe based out of San Francisco. Stripe is a payments processing platform for the internet and I’ve been working at Stripe for the last two and a half years as a full stack product engineer and currently on a team building internal collaboration tooling. Prior to Stripe, I worked at a couple other startups. I’ve actually worked at three different companies in the first three years of my career.
Judith Syau: The thing about startups and smaller companies is that it’s really hard to get a good sense of what working at a company is like unless you personally know someone there, which is why I’m here today, to share strategies you can use to research company culture so it’s less daunting to go out of your comfort zone and consider you’re working at a company that you don’t know much about.
Judith Syau: In today’s session, I’ll be covering ways to research company culture throughout the entire interview process, starting from networking strategies before you apply all the way until receiving and negotiating the job offer. And if there is any time left at the end, I’ll also be answering questions in the chat. Definitely keep interacting in the chats and let me know your thoughts throughout the talk. Cool.

Judith Syau: Let’s start off with some networking strategies. Why is networking important? Networking is important for referrals, which get your foot into the door when a cold application doesn’t work. How do you build a network at events such as career fairs, conferences like this one? You can get contact information of not only recruiters at the career fair, but also your peers at networking sessions and follow up afterwards via email or connecting on LinkedIn.
Judith Syau: You never know how valuable a connection is and it could be the key to getting your next job if there are specific places you want to work at. You can search for employees on that you share experiences with, such as people who went to the same college or worked at a previous company together or are part of the same community and use that as a starting point for connecting.
Judith Syau: Often that shared connection is what gets people to respond. So like if you have a mentor at school or work or know someone a little bit more senior than you in their career, you can also leverage their network and ask them to introduce you to people. And there are also several tech communities and groups out there that have job boards, networking and mentorship events. Even if you don’t have an existing community, there are plenty of them online that you can find. If you have a favorite networking strategy that I didn’t mention yet, feel free to share it with others in the chat. Cool.
Judith Syau: After building up a network and scoring the interview, let’s go over some useful questions to ask. First of all, make sure to tailor your question to the who you’re interacting with so that you can get the most useful information. For example, you might be interacting with the recruiter or an interviewer for the same role such as engineer or a potential future manager or a hiring manager. And let’s go over some examples of these questions.
Judith Syau: Questions about the day-to-day job are good to ask someone who shares the same role that you are interviewing for such as an engineer. You could ask what are your favorite or least favorite parts about the job? What is the most stressful part about your job? Or what is the on-call rotation like? For example, if you’re working on a team or product that’s supporting multiple regions across the the globe, different countries, different time zones, you might be getting paged at odd hours and that’s something that you might want to think about before you accept the job offer.
Judith Syau: And then you should also ask people how they would describe their work-life balance. For example, right now I can tell you that I can make time for it to take a brush painting class at 3:00 PM on Tuesdays and Thursdays. This means I can shift my schedule to work East Coast hours on parts of the week. I also block out some time in my schedule to volunteer to teach a high school computer science class on Friday mornings. A couple years ago when I began my career, my answer to that question would be very different. I would say that I often stay late at the office for free dinner at 7:00 PM and then play board games with my coworkers afterwards. So, work-life balance goals might be very different at different stages of your life.
Judith Syau: Questions about diversity, equity, and inclusion are good to ask recruiters. They often have the most up to date data about this. So for example, you could ask what ERGs or employee resource groups are at the company. For example, this could be like like women or parents or for example my company has like an east and southeast Asian employee resource groups and we do we celebrate like lunar New Year and we have like book clubs and, and things like that.
Judith Syau: Another good question to ask is what is the ratio of underrepresented minorities in leadership? Companies often will like brag about their diversity statistics being, you know, better than average, but the more you go up the career ladder, the more like the more senior and more leadership positions, the more the numbers dwindle. And lastly you can ask what has your company done to support current event? For example, during the Roe versus Wade Supreme Court decision, several companies made public statements about covering abortion related travel expenses. If there’s a current event that might be applicable to you or that you care a lot about you should definitely ask about what the company’s stance is and how, what they’re doing to support employees. Cool
Judith Syau: Next we have career development questions and these are good to ask a hiring manager. A good question to ask is what does it take for someone to be successful in this role? Maybe the manager already has some expectations that they can share with you. This could also be reworded as what would success look like six months down the line? And what advice would you give to someone who just joined?
Judith Syau: And what is the performance review process like? If you are trying to get promoted soon, you you could ask this question to see if the expectations align with what you’re aiming for. And then lastly, an interesting question to ask might be, why is this position open? Maybe the team is trying to backfill someone who left either by choice or not by choice. Or maybe the company is growing really quickly, like they want to double their headcount by the end of the year. And all of this could have implications on the company culture. I know I talked about a lot of interview questions, but there are probably plenty more that would be useful to ask. Share your favorite interview question in the chat if you have one <affirmative>. Cool. Other than asking questions during the interview process, you can also do some research about what public thinks about the company.
Judith Syau: First, let’s start off with company trajectory. Public companies will publish their quarterly earnings call, which shows how their financials perform against expectations. You can also look at how their stock is doing.
Judith Syau: For startups, it’s a bit more complicated because company financials are private and Crunchbase is an online resource that shows the series of a startup startups fundings and valuations, which is how much investors think the startup is worth. Down rounds are when a company raises money at a lower valuation than they did previously, which might indicate that they are not doing so well.
Judith Syau: However, keep in mind about the macroeconomic situation as well. For example, it’s possible that all tech companies are not doing well at a certain point in time, or certain spaces might be having a particularly hot moment like AI is right now. And not too long ago there was web3, so there are always trends in tech, some are successful long term and others might have up and downs. And you should keep all of this in mind
Judith Syau: For a public image, you can look at news articles about the industry including peer companies and competitors. For example, I work in the FinTech space, so I’m always keeping up with news about other FinTech companies. Also, company policies and reactions towards global events such as return to office policies or layoffs can be pretty indicative of the culture as well. For example, like their messaging towards departing employees or even just how they are, they treat their departing employees. Many founders and leaders are super active on social media and some of them even write blog posts and those are pretty telling of how they run their business. This could be from their like Twitter accounts to like each company’s blog section. And lastly, some companies will list their values on their website and that often defines their culture as well.
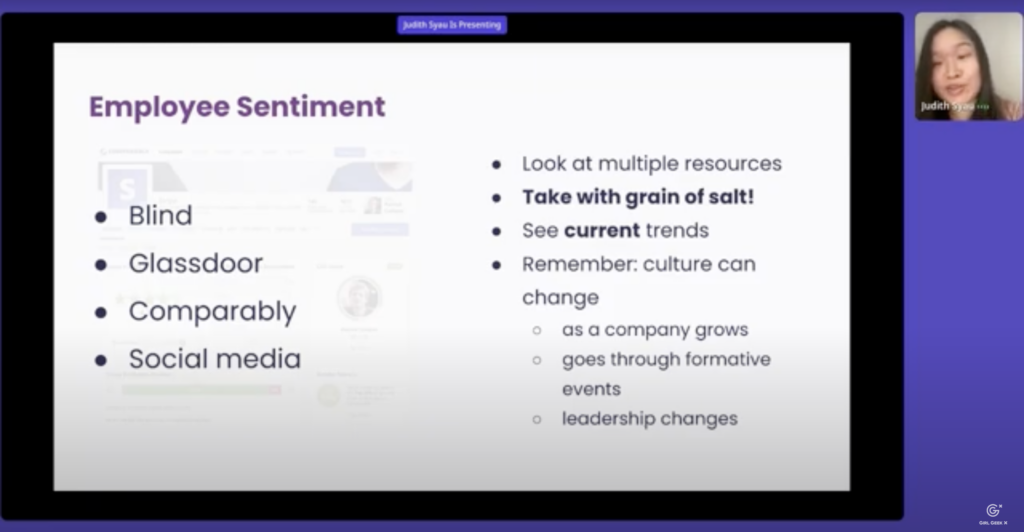
Judith Syau: Now that we know what the public thinks, how do employees themselves feel about the company? There are several online resources that reveal employee sentiment and I’ll share a few here. Blind is an anonymous forum where people can chat about their tech companies and it requires your company email to sign up. Glassdoor is very similar and has anonymous employee reviews. Comparably is a report card that rates company culture based on several employee reported factors. And lastly, we have social media where influencers post content about their role in tech.
Judith Syau: It’s important to look at multiple resources and remember to take them with a grain of salt. Someone who posts anonymously will have a very different agenda than someone who’s posting on their personal social media for their image. But one thing you can look at is current trends. Maybe if a bunch of employees are feeling a certain way about a policy that was implemented in like the last six months, that might be super relevant to you, but something that was had that happened like five years ago is probably not as relevant. Always remember that culture can change as a company grows or goes through formative events or goes through leadership changes.
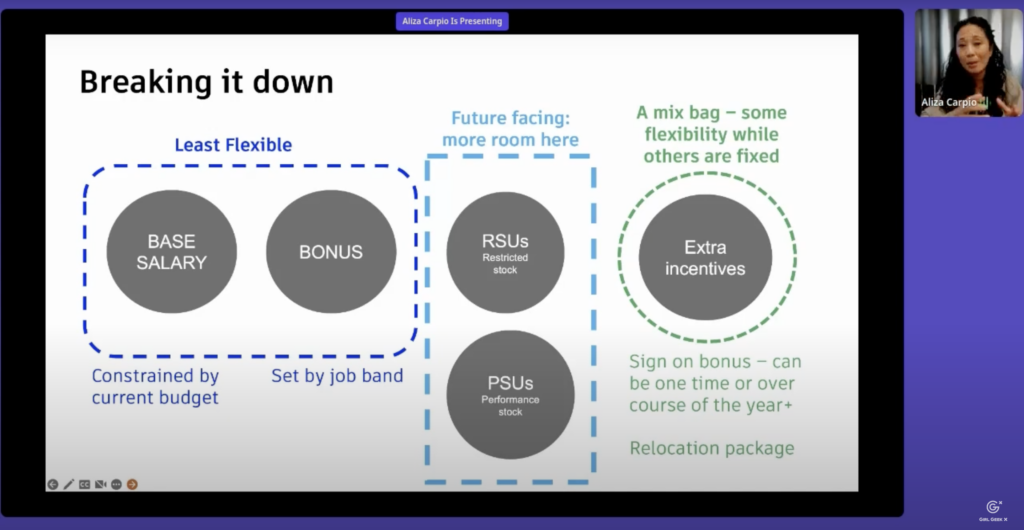
Judith Syau: Let’s say you’ve done all your research and have an offer in hand. How do you make sure that you are getting paid what you’re worth? The first thing about offer compensation is to always negotiate. Every component can be negotiated including salary, stock and bonus. And you don’t know unless you try you might be even able to negotiate other benefits or maybe working hours or even your level at the company.
Judith Syau: And even if you don’t have competing offers, you can still look at data and use that to negotiate and see if you are getting a fair deal. Let’s so there are several crowdsource databases on available online. The first one that I really like is levels.fyi and I like this because not only does it show the different components of compensation such as salary, stock and bonus, it also shows people’s levels as well as their years of experience.
Judith Syau: I’ve personally, I’ve successfully negotiated my level when I accepted an offer before. That is something you could look at like to see if your years of experience line up to the offer that you’re getting. Glassdoor also has has a lot of anonymously reported salary information as well as LinkedIn and candor. Someone in the chat asked a question – are these tips more geared towards large or established companies? For a lot of these resources, obviously there will be more data on large companies, but personally I’ve used these to interview at small startups and surprised like what information you can find out there. I think the tech community is very big and a lot of people will be interviewing or talking to the same companies even if they are very small.
Judith Syau: For governments jobs, they publish all of their salaries online, it’s public information and if the company sponsors H-1B visas, the H-1B visa salaries are also all available online. And if you live in a state that has salary transparency laws, for example, California now requires all companies to publish like a salary range for the role. That’s super important information that you can leverage. Some other states might have be required to reveal the salary ranges if you ask them or if you pass the interview a certain interview stage. Definitely look up the applicable laws for your state that you live in and use that to your advantage. And for startups it’s a little bit more complicated because a big component of the compensation is equity. And for this, there’s a super useful guide online called Holloway’s Guide to Equity Compensation that shares like what is reasonable percentage of equity to expect at different stages of a company.
Judith Syau: And definitely share any other information you might have in the chats that I haven’t listed above. Hopefully you’ve learned something valuable in this session and are able to apply a combination of these strategies to understand company culture a little bit better and maybe even use that during the career fair later on today. Thank you all for joining. I’ll be answering questions in the chat for the remainder of the time. I think we might be at time. Feel free to stick around or use or contact me on LinkedIn or via my email. And hope you’ll enjoy the rest of the summit.
Angie Chang: Thank you Judith. That was really a great talk on company culture and how to evaluate. I like the part about networking to get your foot in the door, especially if you don’t have a referrals or an in in the industry. It’s a great way to get that in. There’s plenty of people here who will like to refer somebody, so I’m gonna say thank you so much for joining us and we’re gonna be hopping over to our next session soon. Thank you, Judith.
Like what you see here? Our mission-aligned Girl Geek X partners are hiring!
- Check out open jobs at our trusted partner companies.
- Watch all ELEVATE 2023 conference video replays!
- Does your company want to sponsor a Girl Geek Dinner? Talk to us!